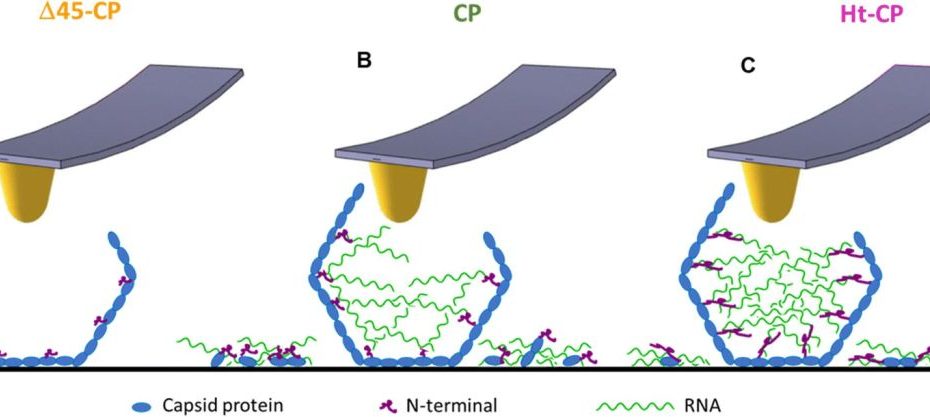
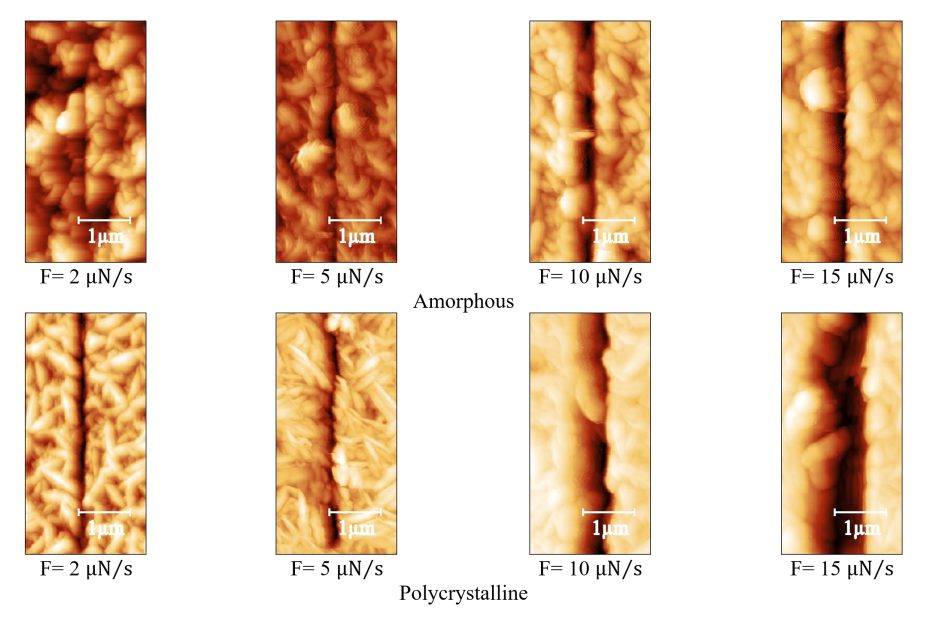
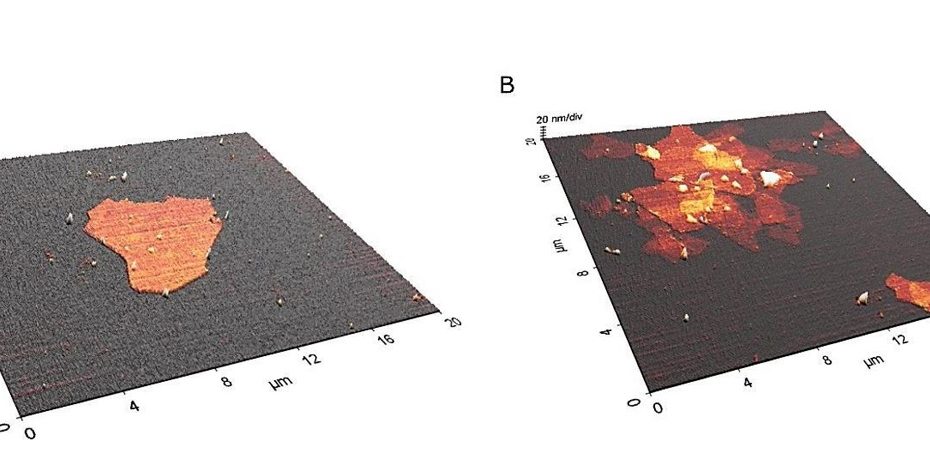
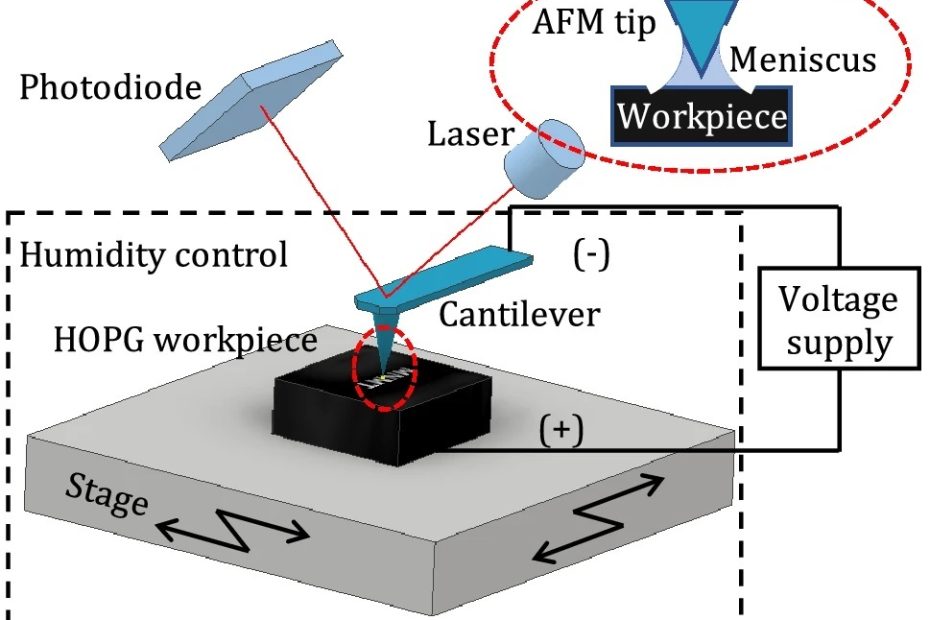
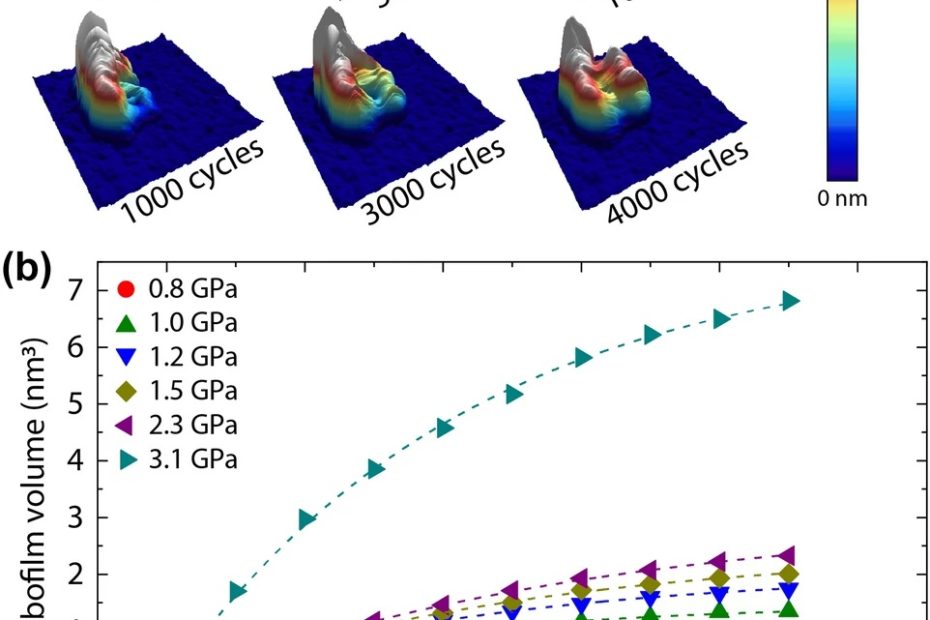
Mechanical disassembly of human picobirnavirus like particles indicates that cargo retention is tuned by the RNA-coat protein interaction
The idea of using virus-like particles as nanocarriers for heterologous cargo transport and delivery requires controlling the stability of the container–cargo system.* In particular, the… Read More »Mechanical disassembly of human picobirnavirus like particles indicates that cargo retention is tuned by the RNA-coat protein interaction