Yucheng Yang, Kaikui Xu, Luke N. Holtzman, Kristyna Yang, Kenji Watanabe, Takashi Taniguchi, James Hone, Katayun Barmak and Matthew R. Rosenberger
Atomic Defect Quantification by Lateral Force Microscopy
ACS Nano 2024, 18, 9, 6887-6895
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.3c07405
Irene C. Turnbull and Angelo Gaitas
Characterizing induced pluripotent stem cells and derived cardiomyocytes: insights from nano scale mass measurements and mechanical properties
Nanoscale Advances, 2024, 6, 1059-1064
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D3NA00727H
Eleni Dalaka, Joseph S. Hill, Jonathan H. H. Booth, Anna Popczyk, Stefan R. Pulver, Malte C. Gather and Marcel Schubert
Deformable microlaser force sensing
Light: Science & Applications (2024) 13:129
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-024-01471-9
Perrine Verdys, Javier Rey Barroso, Adeline Girel, Joseph Vermeil, Martin Bergert, Thibaut Sanchez, Arnaud Métais, Thomas Mangeat, Elisabeth Bellard, Claire Bigot, Catherine Astarie-Dequeker, Arnaud Labrousse, Jean-Philippe Girard, Isabelle Maridonneau-Parini, Christel Vérollet, Frédéric Lagarrigue, Alba Diz-Muñoz, Julien Heuvingh, Matthieu Piel, Olivia du Roure, Véronique Le Cabec, Sébastien Carréno and Renaud Poincloux
Ezrin, radixin, and moesin are dispensable for macrophage migration and cellular cortex mechanics
EMBO Journal (2024)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44318-024-00173-7
Irene C. Turnbull, Apratim Bajpai, Katherine B. Jankowski and Angelo Gaitas
Single-Cell Analysis of Contractile Forces in iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes: Paving the Way for Precision Medicine in Cardiovascular Disease
International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24(17)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713416
Min Ye, Yiran Shan, Bingchuan Lu, Hao Luo, Binhan Li, Yanmei Zhang, Zixuan Wang, Yuzhi Guo, Liliang Ouyang, Jin Gu, Zhuo Xiong and Ting Zhang
Creating a semi-opened micro-cavity ovary through sacrificial microspheres as an in vitro model for discovering the potential effect of ovarian toxic agents
Bioactive Materials, Volume 26, August 2023, Pages 216-230
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.02.029
Dr. Hassiba Smida, François-Xavier Lefèvre, Dr. Christine Thobie-Gautier, Dr. Mohammed Boujtita, Dr. Catarina M. Paquete and Dr. Estelle Lebègue
Single Electrochemical Impacts of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 Bacteria for Living Cells Adsorption onto a Polarized Ultramicroelectrode Surface
ChemElectroChem, Volume 10, Issue 1, January 2, 2023, e202200906
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.202200906
Shotaro Tanaka and Fumio Nakamura
Exploring the Bio-Functional Breaking Point of Living Tissue Subjected to External Physical Pressure
Journal of Robotics and Mechatronics Vol.34 No.2, 2022
DOI: https://doi.org/10.20965/jrm.2022.p0319
Arnaud Millet
A Universal Model for the Log-Normal Distribution of Elasticity in Polymeric Gels and Its Relevance to Mechanical Signature of Biological Tissues
Biology 2021, 10(1), 64
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10010064
Johannes Rheinlaender, Andrea Dimitracopoulos, Bernhard Wallmeyer, Nils M. Kronenberg, Kevin J. Chalut, Malte C. Gather, Timo Betz, Guillaume Charras, and Kristian Franze
Cortical cell stiffness is independent of substrate mechanics
Nature Materials volume 19, pages 1019–1025 (2020)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-020-0684-x
M. Rigby, M. Anthonisen, X. Y. Chua, A. Kaplan, A. E. Fournier and P. Grütter
Building an artificial neural network with neurons
AIP Advances 9, 075009 (2019)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5086873
Joanna Dziadkowiec, Bahareh Zareeipolgardani, Dag Kristian Dysthe and Anja Røyne
Nucleation in confinement generates long-range repulsion between rough calcite surfaces
Nature Scientific Reports volume 9, Article number: 8948 (2019)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45163-6
Chao-Hung Chang, Hsiao-Hui Lee and Chau-Hwang Lee
Substrate properties modulate cell membrane roughness by way of actin filaments
nature Scientific Reports volume 7, Article number: 9068 (2017)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09618-y
Tânia Lourenço, Joana Paes de Faria, Christian A. Bippes, João Maia, José A. Lopes-da-Silva, João B. Relvas and Mário Grãos
Modulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation and maturation by combined biochemical and mechanical cues
nature Scientific Reports volume 6, Article number: 21563 (2016)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21563
Venkata Arun Timmaraju, Priyanka A. S. Theophilus, Kunthavai Balasubramanian, Shafiq Shakih, David F. Luecke and Eva Sapi
Biofilm formation by Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato
FEMS Microbiology Letters, Volume 362, Issue 15, August 2015, fnv120
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnv120
James W. Foster, Roanne R. Jones, Christian A. Bippes, Ricardo M. Gouveia and Che J. Connon
Differential nuclear expression of Yap in basal epithelial cells across the cornea and substrates of differing stiffness
Experimental Eye Research, Volume 127, October 2014, Pages 37-41
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2014.06.020







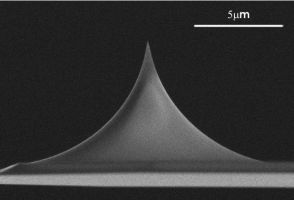
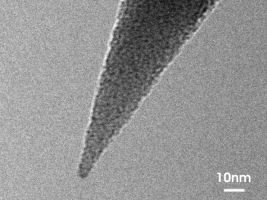
 Due to their unique geometry the tips of the uniqprobes are more susceptible to tip damage by electrostatic discharge (ESD) than other Silicon-SPM-Probes.
Due to their unique geometry the tips of the uniqprobes are more susceptible to tip damage by electrostatic discharge (ESD) than other Silicon-SPM-Probes.